The Prospects of Used Electric Cars in Developing Countries open up an exciting narrative about the shifting landscape of transportation in regions where innovation meets necessity. As the world moves towards sustainability, developing countries are beginning to recognize the potential of used electric cars as a viable alternative to traditional vehicles. With rising fuel prices and urban pollution, the adoption of electric cars not only presents an economic opportunity but also a step towards a greener future.
The current state of electric car adoption in these regions shows promising growth, supported by various statistics highlighting sales trends and the increasing interest in eco-friendly transportation solutions. Several factors, including economic incentives and environmental awareness, are steering this movement, making it a topic worth exploring.
Overview of Electric Cars in Developing Countries
The landscape of electric cars in developing countries is rapidly evolving, reflecting both the global shift towards sustainable transportation and the unique challenges these regions face. While electric vehicle (EV) adoption has historically lagged behind more developed nations, recent trends indicate a significant uptick in interest and investment in this sector.The current state of electric car adoption in developing regions varies widely, influenced by factors such as government policies, infrastructure development, and economic conditions.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the global sales of electric vehicles reached 6.6 million units in 2021, and developing countries accounted for approximately 25% of this total. Countries like China and India are leading the charge, with China alone seeing EV sales surge to over 3 million in 2021, representing a 169% increase from the previous year. This surge is largely driven by government incentives, improvements in battery technology, and rising fuel prices, which have made electric vehicles more appealing to consumers.
Factors Influencing the Growth of Electric Cars
Several key factors are contributing to the growth of electric cars in developing countries, shaping both the market and consumer behavior. Understanding these factors is essential for recognizing the broader implications of this automotive evolution.
- Government Incentives: Many developing nations are implementing tax breaks, rebates, and subsidies to encourage EV adoption. For instance, India has launched the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME) scheme, which provides financial incentives for consumers purchasing electric vehicles.
- Infrastructure Development: The growth of charging infrastructure is critical for the acceptance of electric cars. Countries like South Africa are investing in expanding their charging networks to alleviate range anxiety for potential EV buyers.
- Environmental Awareness: As awareness of climate change grows, more consumers in developing countries are seeking eco-friendly transportation options. This cultural shift is pushing governments and businesses to focus on electric mobility solutions.
- Economic Considerations: With fluctuating fuel prices, electric vehicles present a cost-effective alternative for daily commuting. In regions where gasoline prices are high, like many areas in Latin America, the demand for electric cars is increasing due to potential savings on fuel costs.
- Local Manufacturing: Several developing countries are beginning to establish local electric vehicle manufacturing facilities, reducing costs and increasing access to electric vehicles. For example, Ethiopia has engaged in partnerships to produce electric buses locally, fostering job creation and economic growth.
“The transition to electric vehicles represents not just a shift in technology but a fundamental change in how we approach transportation sustainability in developing nations.”
Economic Factors Influencing Electric Car Adoption
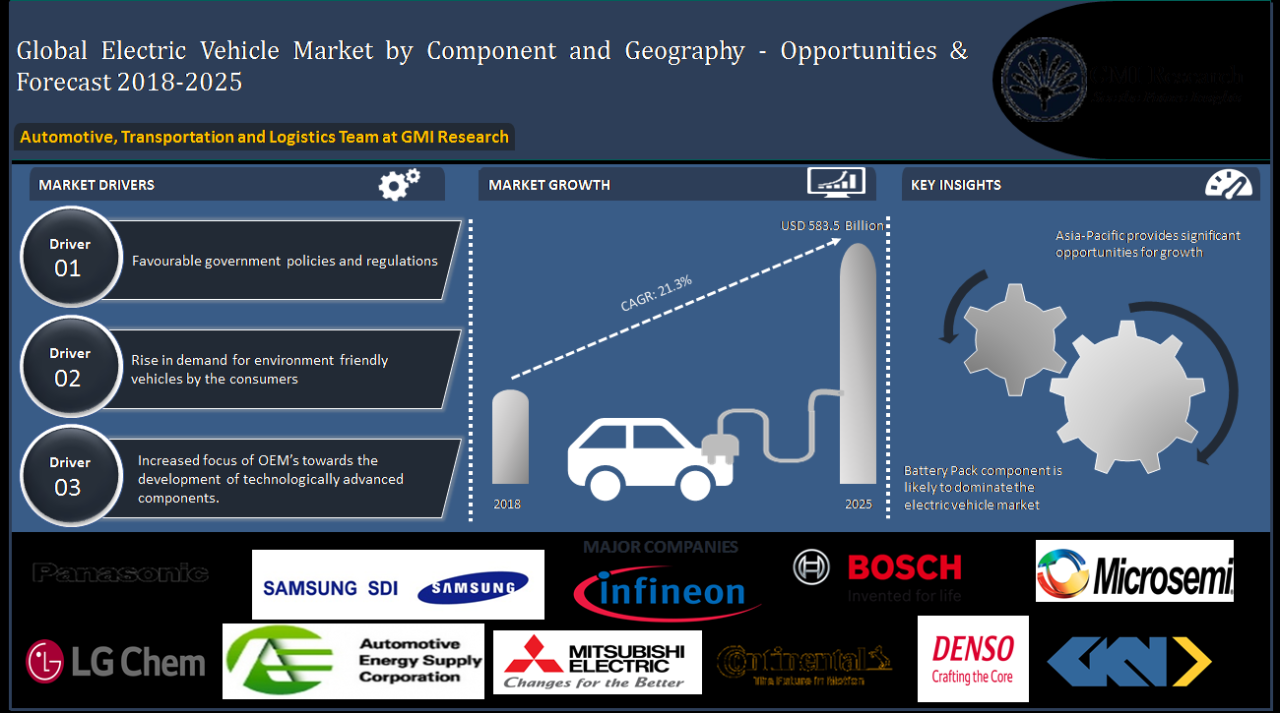
The adoption of electric cars in developing countries is heavily influenced by various economic factors. Understanding these aspects is crucial for both consumers and policymakers as they navigate the evolving automotive landscape. This section delves into the economic benefits presented by electric vehicles (EVs) compared to traditional vehicles, the implications of ownership costs, and the role of government incentives in promoting EV usage.
Economic Benefits of Electric Cars
Electric cars offer several economic advantages over their traditional gasoline-powered counterparts. These benefits are not only significant for individual owners but also contribute to broader economic and environmental goals.
- Lower Fuel Costs: Electric vehicles typically have more affordable energy costs. For instance, charging an EV can be significantly cheaper than fueling a gasoline vehicle, especially in regions where electricity generation is based on renewable sources.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: EVs generally require less maintenance than conventional vehicles due to fewer moving parts. For example, electric cars do not need oil changes, and brake wear is reduced due to regenerative braking systems.
- Long-term Savings: Over time, the cumulative savings from lower fuel and maintenance costs can outweigh the higher initial purchase price of electric vehicles, making them a financially savvy choice.
Cost Implications of Ownership
Understanding the total cost of ownership is essential for potential electric car buyers. The initial costs versus the long-term savings can significantly influence purchasing decisions.The financial implications of owning an electric car include:
- Upfront Investment: While electric cars can have a higher initial price, many consumers are finding that available financing options and subsidies can mitigate this.
- Depreciation Rates: Electric vehicles often depreciate slower than traditional vehicles, particularly as the market for used EVs grows, making them a sound investment.
- Incentives: Many governments provide tax breaks or incentives for electric car buyers, further reducing the effective purchase price and enhancing the appeal of EVs.
Government Incentives and Policies
Government intervention plays a crucial role in accelerating electric vehicle adoption through various incentives and policies that encourage consumers and manufacturers alike.The following government initiatives can significantly impact electric car adoption:
- Tax Credits: Many countries offer tax credits for electric vehicle purchases, which can lower the effective cost by thousands of dollars.
- Infrastructure Development: Investment in charging infrastructure is vital, with governments often leading initiatives to expand charging networks, making EVs more practical for everyday use.
- Regulatory Support: Policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions, such as stricter emissions standards for traditional vehicles, can bolster the attractiveness of electric vehicles.
“The transition to electric vehicles not only supports environmental goals but also presents significant economic opportunities for consumers and nations alike.”
The combination of these economic factors can greatly influence the adoption rates of electric vehicles in developing countries. As the market evolves, these considerations will remain central to understanding the future of sustainable transportation.
Environmental Impact of Used Electric Cars
The shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) is more than just a trend; it’s a crucial step in reducing the environmental footprint of transportation. Used electric cars, in particular, offer a sustainable option for developing countries where the transition to cleaner energy is pivotal. By integrating used EVs into the market, these regions can enjoy significant ecological benefits while addressing the pressing challenges of urban air quality and climate change.Electric vehicles are known for their potential to drastically lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles.
This shift is especially vital for developing nations, where air pollution and associated health risks are exacerbated by dense traffic and outdated vehicle technology. Transitioning to used electric cars can lead to remarkable reductions in emissions, as they produce zero tailpipe emissions and typically operate on cleaner energy sources.
Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The reduction in greenhouse gas emissions is a primary ecological advantage of transitioning to electric vehicles. Electric cars contribute to a significant decrease in carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions when compared with their gasoline or diesel counterparts. The overall lifecycle emissions of electric vehicles, including manufacturing, usage, and disposal, tend to be lower than those of new internal combustion engine vehicles.
The following points highlight the environmental impact of used electric cars:
- Lower Operational Emissions: Used electric cars produce no tailpipe emissions, which directly improves air quality in urban areas where pollution levels are critically high.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: The carbon footprint of electric vehicles, when charged with renewable energy, can be substantially lower compared to traditional vehicles, especially when considering the entire lifecycle from production to end-of-life.
- Energy Efficiency: Electric cars convert over 60% of the electrical energy from the grid to power at the wheels, significantly more efficient than conventional gas vehicles, which only convert about 20% of the energy stored in gasoline.
The cumulative effect of these factors leads to substantial reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, not only during the operation of the vehicle but also throughout its life cycle.
“Transitioning to electric vehicles has the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 70% over their lifetime, particularly when paired with renewable energy sources.”
By embracing used electric cars, developing countries can play an active role in combating climate change while simultaneously improving public health and urban air quality. The broader adoption of EVs can help meet global climate targets and foster a more sustainable future for generations to come.
Challenges in the Used Electric Car Market: The Prospects Of Used Electric Cars In Developing Countries
The adoption of used electric cars in developing countries is hindered by a variety of challenges that complicate their integration into the existing transportation system. While the potential benefits of used electric vehicles (EVs) are substantial, structural and societal barriers remain significant impediments to widespread acceptance and use. Addressing these challenges is essential to harnessing the full potential of electric mobility in these regions.Infrastructure challenges play a crucial role in the limited traction of used electric cars.
The lack of adequate charging stations is a primary concern, as potential buyers often fear being unable to recharge their vehicles conveniently. Furthermore, maintenance facilities equipped to service electric vehicles are scarce, leading to doubts about the long-term viability of owning a used EV. This lack of infrastructure not only affects consumer confidence but also impacts the resale value of electric cars.
Infrastructure Challenges and Misconceptions
The absence of a robust infrastructure to support used electric vehicles manifests in several key areas that need attention. Firstly, the charging network is underdeveloped in many developing countries, making it difficult for owners to find convenient charging locations. Additionally, the limited number of trained technicians familiar with electric vehicle technology can discourage potential buyers from considering used EVs.To further understand the hesitations surrounding used electric cars, it’s beneficial to address common misconceptions held by potential consumers.
Recognizing these misunderstandings can facilitate a more informed decision-making process regarding electric vehicles.
| Common Misconception | Reality |
|---|---|
| Used electric cars are unreliable. | Many used EVs have been well-maintained and can offer excellent performance. |
| Charging takes too long. | Fast chargers can recharge most EV batteries in under an hour, while home charging can be done overnight. |
| Used electric cars have limited range. | Many modern used EVs can now cover over 200 miles on a single charge, suitable for most daily needs. |
| Electric cars are too expensive to maintain. | EVs typically have lower maintenance costs due to fewer moving parts compared to internal combustion vehicles. |
| Resale value of used EVs is low. | As the market matures, the demand for used EVs is increasing, potentially enhancing their resale value. |
Social Acceptance and Consumer Attitudes
In developing countries, the journey toward electric vehicle (EV) adoption is significantly influenced by social acceptance and consumer attitudes. While awareness of electric cars is growing, understanding how consumers perceive these vehicles within their cultural context is essential for fostering acceptance. Factors such as societal norms, values, and local practices play a pivotal role in shaping consumer choices regarding used electric cars.Consumer perception of electric cars in developing markets often fluctuates between optimism and skepticism.
Many view electric vehicles as a modern and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional gasoline cars. However, concerns about reliability, charging infrastructure, and overall cost can hinder widespread acceptance. In countries where public transportation is the norm, the desire for personal vehicles may be tempered by practicality and economic considerations.
Factors Influencing Acceptance of Electric Vehicles
Several cultural and social factors can enhance consumer confidence in purchasing used electric cars. Understanding these factors is crucial for policymakers, manufacturers, and marketers aiming to increase EV adoption. Below are some key elements that can positively influence consumer attitudes:
- Government Incentives: Subsidies or tax breaks for electric vehicle purchases create financial incentives that promote acceptance.
- Awareness Campaigns: Educational initiatives that highlight the benefits of electric vehicles can alter public perception and increase interest.
- Community Testimonials: Word-of-mouth recommendations from early adopters can significantly influence potential buyers, creating a sense of trust.
- Visibility of Charging Infrastructure: The availability and accessibility of charging stations reassure consumers about the practicality of owning an electric vehicle.
- Environmental Awareness: Growing consciousness about environmental issues can drive consumers towards sustainable choices like electric cars.
- Peer Influence: Social circles and community norms often dictate consumer behavior; seeing peers adopt electric vehicles can lead to a broader acceptance.
- Affordability: Competitive pricing for used electric cars relative to traditional vehicles can make them more attractive to budget-conscious consumers.
Consumer attitudes towards used electric cars are evolving, shaped by a mix of cultural perceptions, economic factors, and the pressing need for environmentally sustainable solutions. Recognizing these influences can aid in creating strategies that resonate with local populations in developing countries, ultimately leading to greater acceptance and adoption of electric vehicles.
Case Studies of Successful Electric Car Integration
The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) is gaining traction in developing countries, where innovative strategies are being implemented to integrate used electric cars into urban settings. Successful case studies provide valuable insights into how these regions are overcoming challenges and enhancing the adoption of electric vehicles. By examining specific examples, we can understand the diverse approaches to promoting EVs and the lessons learned from their implementations.
Successful Examples of Electric Vehicle Adoption
Several cities in developing countries have successfully integrated electric cars into their transportation systems. Notable examples include:
- Santiago, Chile: Santiago has implemented an extensive electric bus fleet, which has dramatically improved air quality and reduced greenhouse gas emissions. The city’s public transport authority collaborated with private companies to develop charging infrastructure and incentivize the use of electric vehicles.
- Nairobi, Kenya: With a focus on sustainable transportation, Nairobi has introduced electric motorcycles as a popular alternative for public transport. The government has provided incentives for riders to switch to electric bikes, leading to a notable reduction in fuel costs and emissions.
- Lagos, Nigeria: Lagos has developed a public-private partnership to introduce electric taxis into its bustling streets. The initiative focuses on creating a network of charging stations and providing subsidies to taxi operators who switch to electric vehicles.
The strategies employed in these case studies vary, yet they share common elements that contribute to their success.
Strategies for Promoting Electric Vehicle Adoption
The strategies for promoting electric vehicle adoption in these regions encompass policy frameworks, financial incentives, and infrastructure development. Each region has tailored its approach to address local needs and conditions.
Public Policy Support
Governments have enacted regulations that promote electric vehicles, including tax breaks, import duty exemptions on electric cars, and investment in charging infrastructure.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Initiatives to educate the public about the benefits of electric vehicles have been crucial. In Santiago, campaigns emphasized the environmental and economic advantages, leading to greater acceptance among citizens.
Partnerships with Private Sector
Collaboration with private companies has facilitated the development of charging networks and maintenance services, as seen in both Lagos and Nairobi.
Financial Incentives
Subsidies and grants for purchasing electric vehicles have made them more accessible. For example, Nairobi’s incentives for electric motorcycle riders have led to a surge in adoption.
Lessons Learned from Successful Initiatives
Analyzing these successful cases reveals several key lessons that can inform future electric vehicle integration efforts:
The Importance of Infrastructure
Reliable and widespread charging infrastructure is essential for the adoption of electric vehicles. Investing in accessible charging stations encourages more users to switch from traditional vehicles.
Community Engagement
Engaging local communities in the planning and implementation of electric vehicle initiatives fosters greater acceptance and support for these programs.
Tailored Solutions
Solutions must be tailored to fit the specific socio-economic conditions of each region. Understanding local needs enhances the effectiveness of deployment strategies.
Long-term Commitment
Successful integration of electric vehicles requires sustained efforts and investments over time. Stakeholders must remain committed to promoting EV adoption through continuous innovation and support.
Holistic Approach
Addressing environmental, economic, and social factors collectively contributes to a more robust framework for electric vehicle adoption, ensuring that all aspects are considered in the integration process.The integration of electric vehicles in developing countries shows promising potential, underscoring the need for innovative strategies and collaborative efforts to foster a sustainable transportation future.
Future Prospects and Innovations
As the global market for electric vehicles (EVs) continues to mature, developing countries stand on the brink of a significant transformation in their transportation landscape. The shift towards used electric cars presents a unique opportunity not only to enhance mobility but also to address economic and environmental challenges. The advent of new technologies, evolving partnerships, and innovative strategies will play a crucial role in shaping the future of used electric cars in these regions.Emerging technologies are set to redefine the used electric car market, making them more accessible and appealing to consumers.
Advancements in battery technology, such as solid-state batteries, promise increased range and reduced charging times, paving the way for broader adoption. Moreover, innovations in vehicle-to-grid technology can enable electric cars to act as energy storage systems, facilitating renewable energy integration and enhancing grid stability.
Potential Partnerships to Boost Adoption
Collaboration among governments, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and the private sector is essential for stimulating the used electric car market. These partnerships can drive initiatives aimed at enhancing infrastructure, ensuring affordability, and increasing public awareness. Such collaborations can take various forms, including but not limited to:
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): These involve joint ventures between governments and private companies to develop charging infrastructure, making electric cars more convenient to use.
- NGO Collaborations: NGOs can facilitate community outreach and education programs to improve understanding and acceptance of electric vehicles.
- Incentive Programs: Governments can partner with private sectors to provide financial incentives like tax breaks or subsidies for purchasing used electric cars.
- Research Initiatives: Collaborative research can yield new technologies and practices that reduce the costs of electric vehicles and their maintenance.
The synergistic effort of these stakeholders will not only enhance the adoption of used electric vehicles but also contribute to a more sustainable and efficient transportation system in developing countries.
Future Predictions for Electric Vehicle Market Growth, The Prospects of Used Electric Cars in Developing Countries
The outlook for electric vehicle growth in developing nations is promising, supported by a combination of technological advancements and strategic partnerships. Below is a table that Artikels future predictions regarding the EV market growth in these regions over the next decade:
| Year | Projected Market Size (in million units) | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|
| 2025 | 1,500 | Government incentives, Increasing charging infrastructure |
| 2030 | 3,000 | Technological advancements, Cost reductions in batteries |
| 2035 | 6,000 | Widespread consumer acceptance, Integration with renewable energy |
The above projections reflect a robust growth trajectory, driven by factors such as improved affordability, increased range, and enhanced convenience. By working together and leveraging new technologies, developing countries can capitalize on the transformative potential of used electric cars, paving the way for a greener future.



